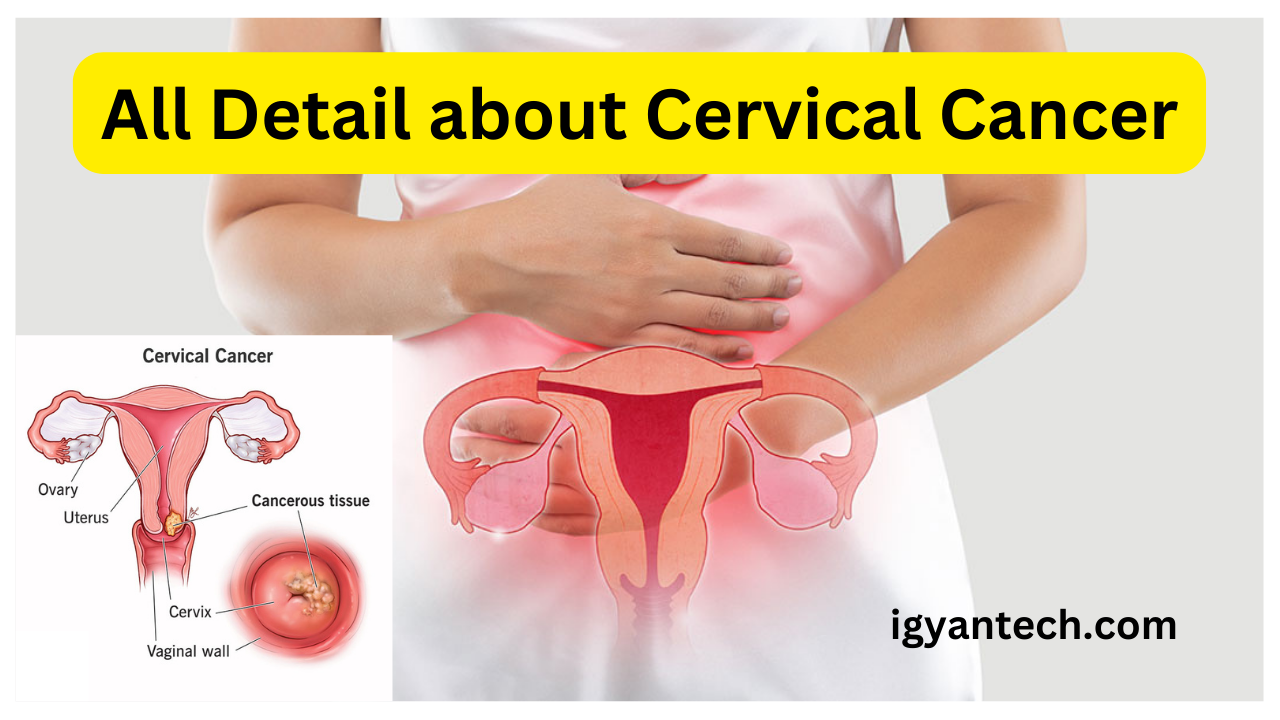
What is cervical cancer? Symptoms of cervical cancer? How to prevent that?
What is cervical cancer? Symptoms of cervical cancer? How to prevent that? all details are discussed here Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that begins in the cervix, which is the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. It is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk strains of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection. Cervical cancer is a significant health concern for women worldwide, but with early detection and prevention measures, its impact can be significantly reduced.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer:
- Abnormal Vaginal Bleeding:
- Unusual bleeding between periods.
- Heavy menstrual bleeding.
- Postmenopausal bleeding.
- Pelvic Pain:
- Persistent pain in the pelvis or lower back.
- Pain During Sexual Intercourse:
- Discomfort or pain during sexual activity.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:
- Rapid and unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue:
- Persistent fatigue and a general feeling of weakness.
- Changes in Menstrual Cycle:
- Changes in the menstrual cycle unrelated to menopause.
- Urinary Symptoms:
- Difficulty or pain during urination.
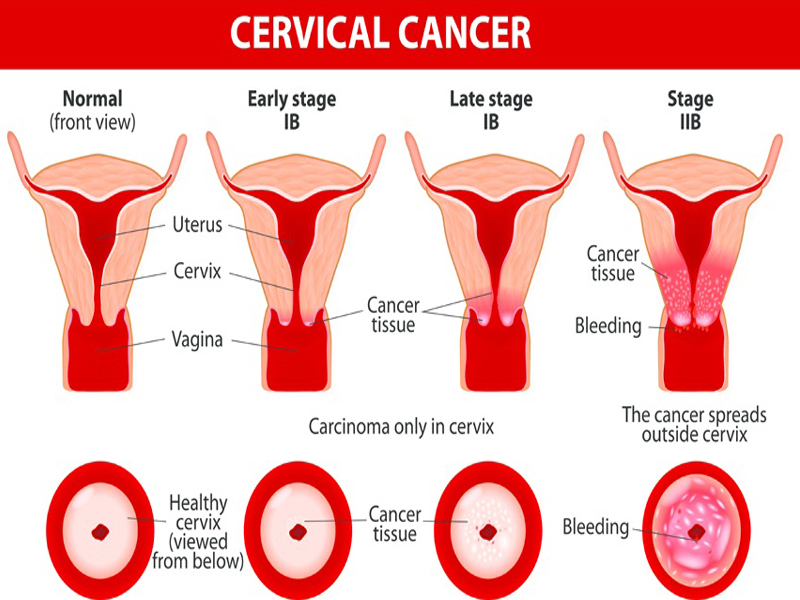
Prevention of Cervical Cancer:
- Vaccination:
- HPV vaccination is a key preventive measure. The vaccine is most effective when administered before any sexual activity.
- It is recommended for both boys and girls, typically between ages 9 and 14.
- Regular Pap Smears:
- Regular screenings with Pap smears or HPV tests can detect precancerous changes in the cervix early on.
- Early detection allows for prompt intervention and increased chances of successful treatment.
- Safe Sexual Practices:
- Practicing safe sex by using condoms can reduce the risk of HPV transmission.
- Limiting the number of sexual partners also decreases the likelihood of exposure to the virus.
- Smoking Cessation:
- Quitting smoking is crucial, as it increases the risk of cervical cancer and interferes with the body’s ability to fight HPV infections.
- Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle:
- A healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and antioxidants can support the immune system.
- Regular exercise contributes to overall well-being and may help reduce the risk of cervical cancer.
- Screening Guidelines:
- Following the recommended screening guidelines for cervical cancer is essential.
- Pap smears are typically recommended every three years for women aged 21 to 29.
- Women aged 30 to 65 may opt for Pap smears every three years or Pap smears combined with HPV testing every five years.
- Educational Initiatives:
- Raising awareness about cervical cancer, its risk factors, and preventive measures is crucial.
- Encouraging routine check-ups and screenings among women can lead to early detection.
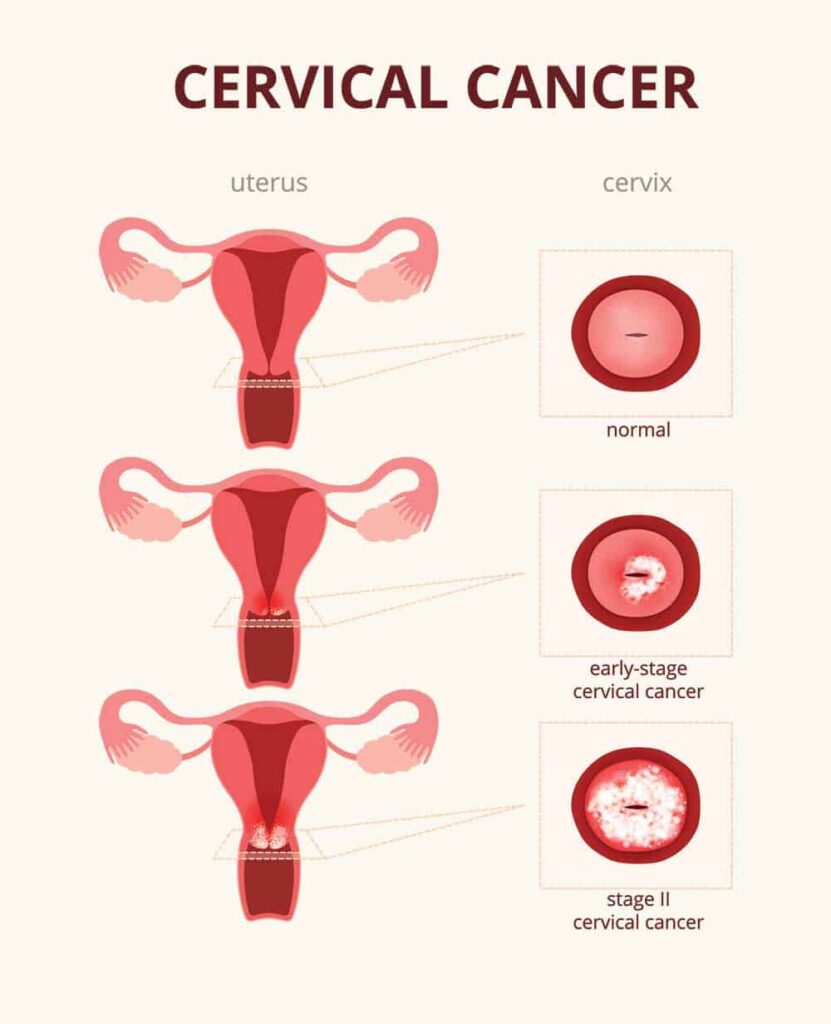
In-Depth Exploration of Cervical Cancer:
1. Risk Factors:
- HPV Infection: Persistent infection with high-risk strains of HPV is the primary risk factor for cervical cancer.
- Smoking: Tobacco use increases the risk of cervical cancer and can lead to more severe disease progression.
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions or medications that suppress the immune system can contribute to the development of cervical cancer.
2. HPV and Cervical Cancer:
- HPV is a group of viruses with over 100 different types, some of which are classified as high-risk for causing cervical cancer.
- The virus is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, and most sexually active individuals will contract HPV at some point.
- In many cases, the immune system clears the infection, but persistent infection with high-risk HPV can lead to the development of cervical cancer.
3. Diagnosis and Staging:
- Diagnosis often involves a Pap smear or HPV test to detect abnormal cells in the cervix.
- If abnormalities are found, further diagnostic procedures such as colposcopy and biopsy may be performed.
- Staging determines the extent of the cancer and helps guide treatment decisions.
4. Treatment Options:
- Treatment modalities for cervical cancer may include surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
- The choice of treatment depends on the stage of cancer, the patient’s overall health, and other individual factors.
- Early-stage cervical cancer is often treated with surgery, such as a hysterectomy or removal of the lymph nodes.
- Advanced-stage cancer may require a combination of radiation and chemotherapy.
5. Psychological Impact:
- A diagnosis of cervical cancer can have significant psychological effects on individuals.
- Support from healthcare professionals, family, and friends is crucial during the treatment and recovery process.
- Mental health support and counseling may be beneficial to address emotional challenges.
6. Ongoing Research and Innovations:
- Ongoing research is focused on improving screening methods, developing targeted therapies, and understanding the role of genetics in cervical cancer.
- Innovations such as immunotherapy are being explored as potential treatment options.
How to Protect Your Teeth from Corrosion?
Conclusion:
Cervical cancer is a significant public health issue that requires comprehensive efforts in prevention, early detection, and treatment. With advancements in medical science, increased awareness, and proactive healthcare measures, the impact of cervical cancer can be mitigated. Vaccination against HPV, regular screenings, and lifestyle modifications play crucial roles in reducing the risk of developing cervical cancer. Additionally, ongoing research and innovations in cancer treatment contribute to the continuous improvement of outcomes for individuals affected by this disease. As a society, promoting education, destigmatizing discussions around women’s health, and ensuring access to healthcare resources are essential steps in the collective effort to combat cervical cancer.